It is important to prevent unplanned pregnancies, especially if you don’t want to have children again. Thankfully, there are a number of ways to achieve this, some of which may be temporary or permanent. An example of a permanent method of birth control is tubal ligation.
Before making a decision to have a tubal ligation done, you need to really understand what it is, what the procedure entails, the pros and cons, and lots more. This knowledge will help guide your decision.
This article has been put together to help you understand in detail what tubal ligation is, when it is advisable, the potential risks involved, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of the procedure.
What is tubal ligation?
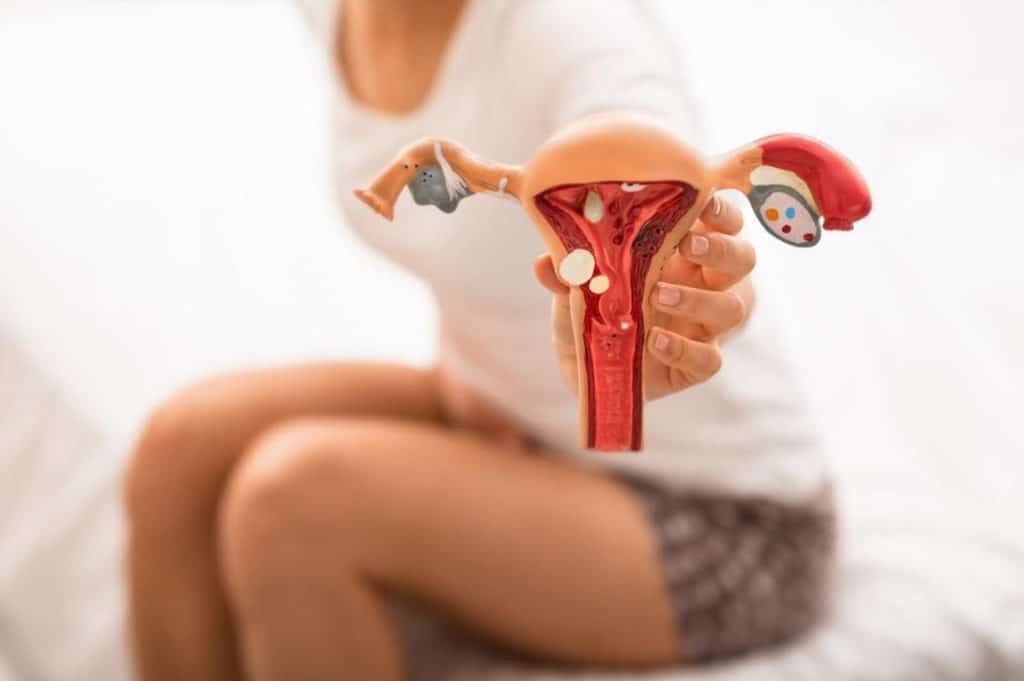
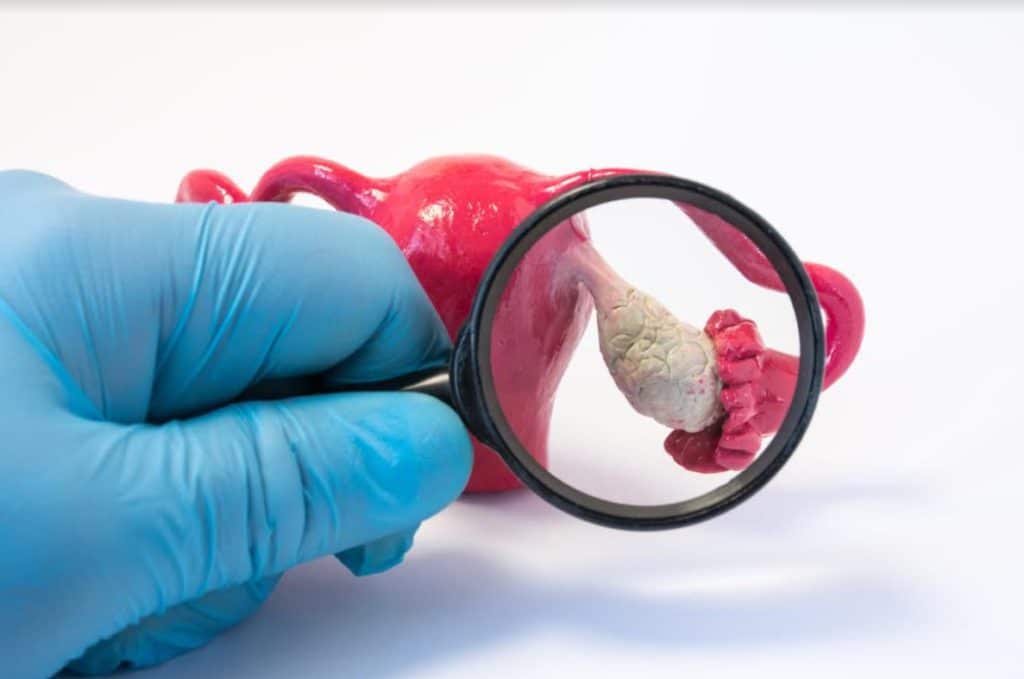
Tubal ligation is also referred to as the “tying of the tubes.” It is a kind of surgery that prevents you from getting pregnant ever again. From the name, tubal refers to the fallopian or uterine tubes, and ligation means tying off.
Your fallopian tubes are thin tubes that connect your ovaries to your uterus and also allow the passage of eggs from the ovaries to your uterus. There are two fallopian tubes, one on each side of the uterus.
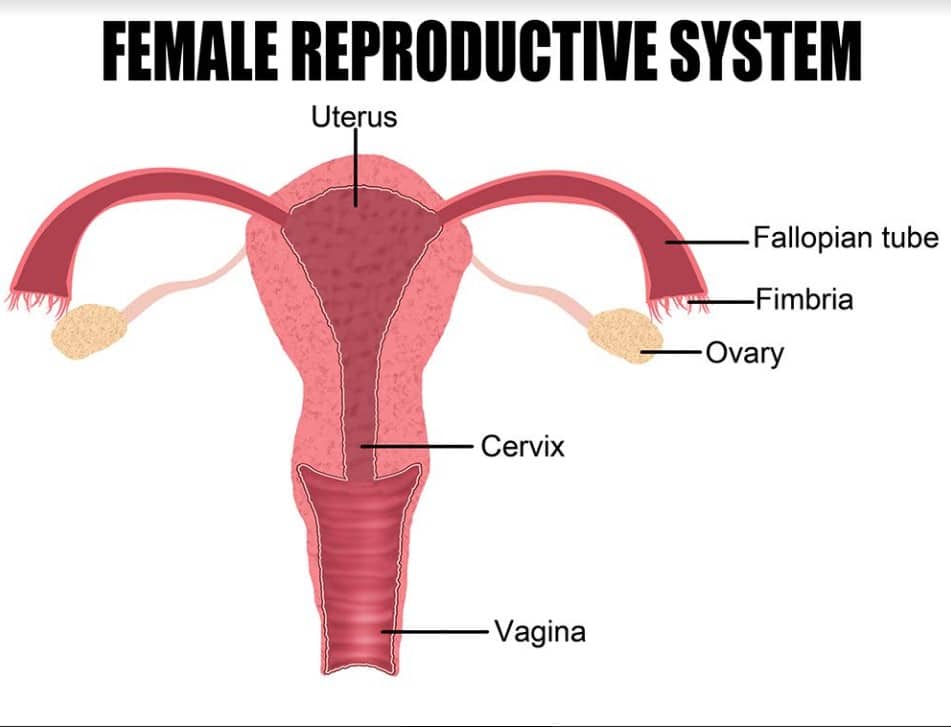
During a tubal ligation, the fallopian tubes are cut or tied to permanently prevent pregnancy from happening. Pregnancy will not happen because a tied or blocked tube will not allow eggs to pass from the ovaries to the uterus, and it will also prevent sperm from moving up the tube to fertilize the egg.
You can also read this post on how to get pregnant without fallopian tubes.
Why tubal ligation?
Tubal ligation is a permanent birth control method for women who do not want to get pregnant again. With this procedure, you don’t need to worry about any type of birth control again.
Other reasons why some women opt for this permanent birth control method include:
- If pregnancy will put them at a health risk i.e. the pregnancy will endanger their life.
- If they or their partners have genetic disorders that they don’t want to pass on to a child.
Risks associated with tubal ligation
Tubal ligation is a surgical procedure and just like other surgical procedures has risks associated with it. Some of the potential risks associated with the procedure are:
- Persistent pelvic or abdominal pain
- Bleeding from the site of the incision or from the abdomen
- Infection at the site of surgery or incision
- Side effects or reactions to the anesthesia used for the surgery
- Injury to the bowel, bladder, or other major organs
The probability of having complications following a tubal ligation is increased in the following cases:
- Previous history of a pelvic or abdominal surgery
- Being overweight or obesity
- Diabetes mellitus
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Lung disease
- Hypertension
Depending on your health status, you may have other side effects aside from the ones listed above. It is important to note, however, that these risks are common to most surgeries, not just this one. Also, as long as a properly trained surgeon performs the procedure, the chances of experiencing any of this are significantly reduced.
Advantages of tubal ligation
It is highly effective
Research has shown that only less than 1% of women get pregnant after having a tubal ligation done. This means that it has worked in more than 99% of cases. Hence, tubal ligation is a very effective method of birth control.
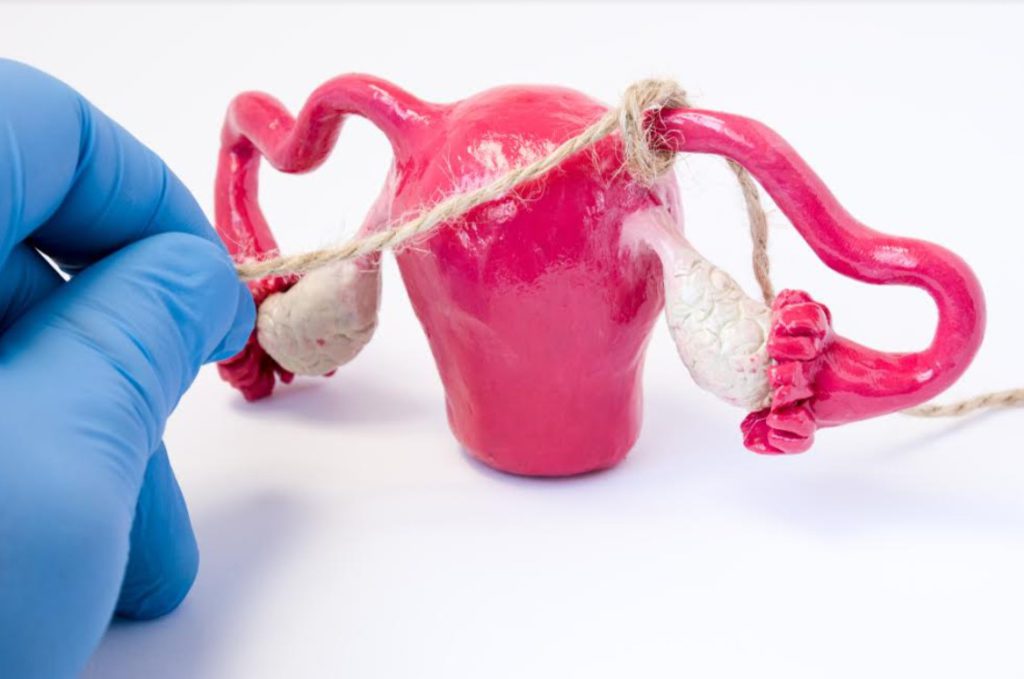

It is a permanent process
With tubal ligation, you don’t have to worry about birth control, either for you or for your partner. It is a permanent process and of great benefit, if you don’t want to have children again.
Tubal ligation does not affect your hormones
Other birth control methods, like hormonal pills or intrauterine devices (IUDs), affect the hormones and cause side effects such as mood swings, weight gain, headaches, cramps, heavy periods, or spotting. Tubal ligation, on the other hand, does not affect the hormones, hence, these side effects do not happen.
It won’t bring changes to your periods or cause menopause.
It lowers the chances of having ovarian cancer
Although the reason for this is not fully understood, studies show that this procedure greatly reduces the chances of having ovarian cancer.
Disadvantages of tubal ligation
Permanence
You must be very sure of what you want before opting for a tubal ligation because once you get a tubal ligation done, you cannot change your mind. The process is not always possible to reverse. In fact, only about 50% of those who had a reversal have been able to get pregnant again.

Pregnancy
It is possible that a tubal ligation will fail, although this is extremely rare. When it does happen, this can result in pregnancy, particularly if the tubes are not completely closed.
No Protection Against STDs
This birth control method only prevents pregnancy, not sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Therefore, you need to put other preventive measures to protect against STDs.
Ectopic pregnancy
On the off chance that a person gets pregnant after a failed tubal ligation, it is possible that the pregnancy will be an ectopic pregnancy, i.e., it is possible that the embryo will implant in other places (like the fallopian tubes) apart from the uterus.
An ectopic pregnancy can lead to severe and life-threatening bleeding if it causes the fallopian tube to burst. In cases like this, urgent or emergency surgery is necessary to fix the problem.
Conclusion
Tubal ligation is a very effective and efficient process to prevent pregnancy. Before opting for a tubal ligation, you should speak with your doctor to determine if it is the best method for you. Also, consider the advantages and disadvantages of going for a tubal ligation.
Remember that a tubal ligation will have no effect on your sexual life or experiences. Following recovery from the surgery, you can return to your normal sexual activities.