Do you remember what it was like the first time you felt your baby kick? It initially feels like flutters or brushes on the inside of your tummy and as the baby grows becomes full-on punches, swishes, and rolls, often visible on your tummy.
The first kicks felt are called “quickening” and mum’s feel this for the first time between 16-24 weeks into their pregnancy.

The well-being of your unborn baby can be monitored at home using a fetal kick count chart especially once you are past 28 weeks pregnant (third trimester).
How do you do it?
Timing: The best time is to schedule this at the same time every day, preferably in the evening once you are done with your chores and can lie down.
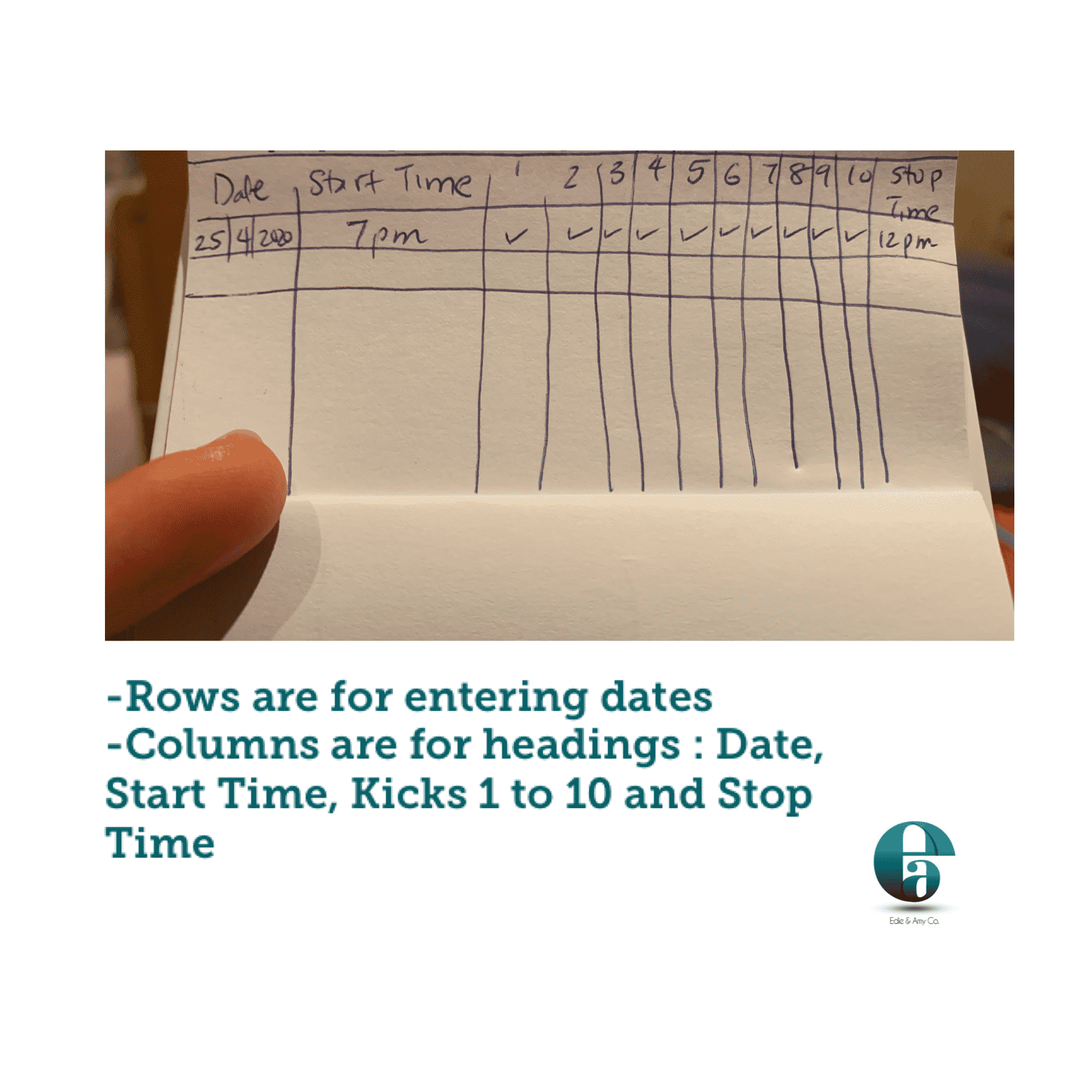
Get a pen and paper, and note the time you want to start. Lie down on your left side, and while lying down make a tick each time baby makes a full range of motion and stops. This is 1 kick.

Once you have gotten 10 kicks, stop and note the time again. You expect 10 of these kicks in at most 12 hours (this is the Cardiff method).
If you don’t get up to 10, have a glass or two of water and try again in an hour.
Do you need to monitor your baby’s movements?
Mums who have been told they have diabetes, hypertension or have had a difficult pregnancy or classified as high risk need to pay more attention to their baby’s movements.
What to do if you feel kicks are less than usual?
First of all, do not panic.
Call your doctor or midwife as soon as possible. They will interview you to assess how you are doing and if you need to come in for further checks which may include an ultrasound scan, listening for your baby’s heartbeat, and so on.
Have you used a fetal kick chart before? It’s easy to create.
References :
WHO recommendation on daily fetal movement counting
RCOG Guideline on reduced fetal movements
Counting Fetal Kicks: Too much info?
See also: Why Your Baby Sleeps The Way They Do