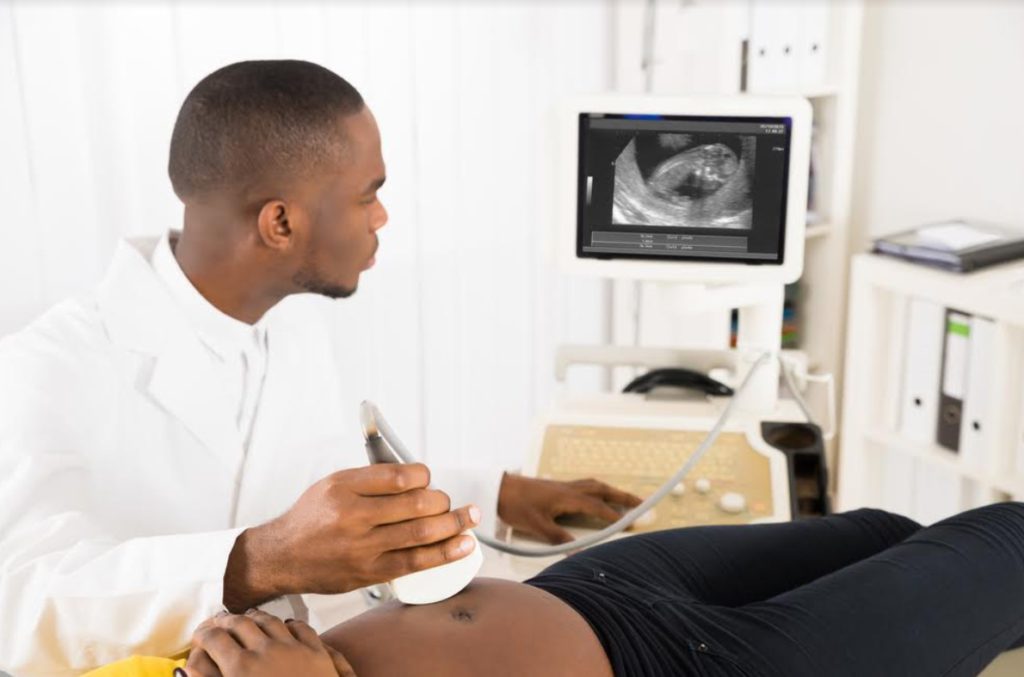
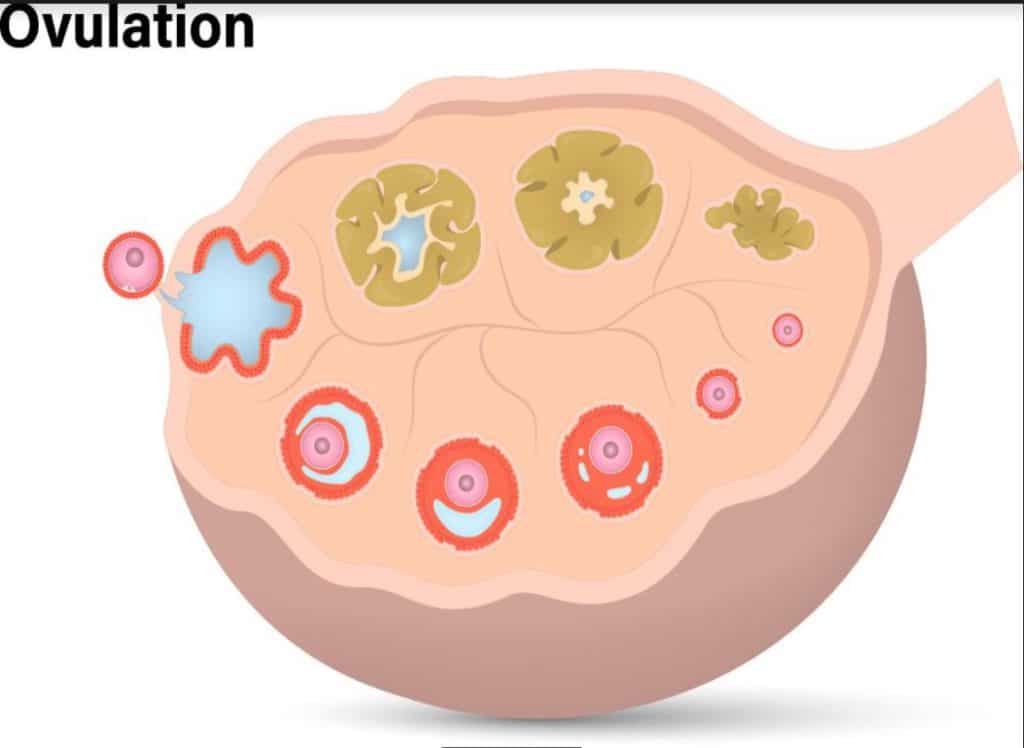
An intrauterine pregnancy (IUP), or uterine pregnancy, occurs when a fertilized egg implants and begins to develop within the uterus, where it should be. This is really important because pregnancy can only develop and progress to full term in the uterus.
In this article, you’ll learn all there is to know about intrauterine pregnancy; the process, confirmation, and possible complications.
Keep reading.
Intrauterine Prengancy
An intrauterine pregnancy discovered via ultrasound indicates that the pregnancy is developing in the proper location.

Early pregnancy symptoms, such as abdominal or pelvic pain and vaginal bleeding, should be investigated to determine the location of the pregnancy and rule out any complications. Ectopic pregnancies develop elsewhere in the female reproductive tract (cervix, ovary, fallopian tubes) and are not viable, meaning they will not result in the birth of a child.
You can also read this post to learn more about ectopic pregnancy.
Intrauterine pregnancy is the desired conception outcome for most couples wishing to have a child. However, it is vital to understand the various stages of intrauterine pregnancy and its potential risks.
Process of intrauterine pregnacy
Intrauterine pregnancy begins when the ovary releases a mature egg during ovulation and this egg travels through the fallopian tube toward the uterus. If the egg is fertilized by a sperm cell during this journey, it forms a zygote, which then travels down the fallopian tube and implants in the lining of the uterus.
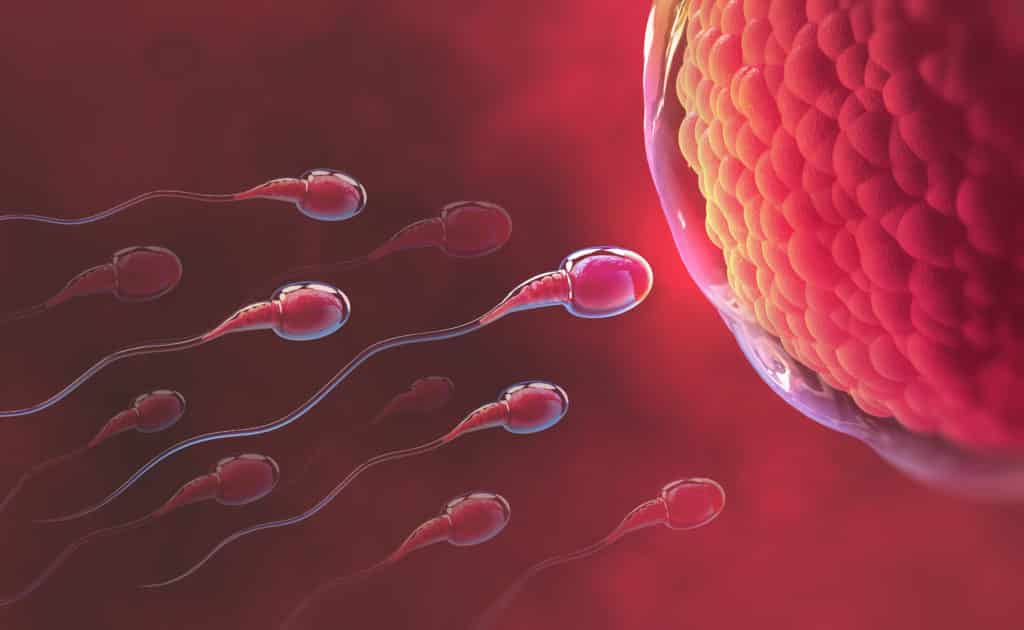
This implantation usually occurs around 6-10 days after fertilization.
The embryo’s development characterizes the early stages of intrauterine pregnancy. The first two weeks after implantation are known as the germinal stage, during which the zygote divides and forms a ball of cells known as a blastocyst. The blastocyst then implants more deeply into the uterine lining, forming the placenta and embryonic tissues.
At around five weeks of gestation, the embryo develops a heartbeat and takes on a recognizable human form. This is also when the placenta starts to produce hormones that support the pregnancy, such as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). Over the next few weeks, the embryo develops various organ systems, including the central nervous, heart, lungs, and digestive systems.
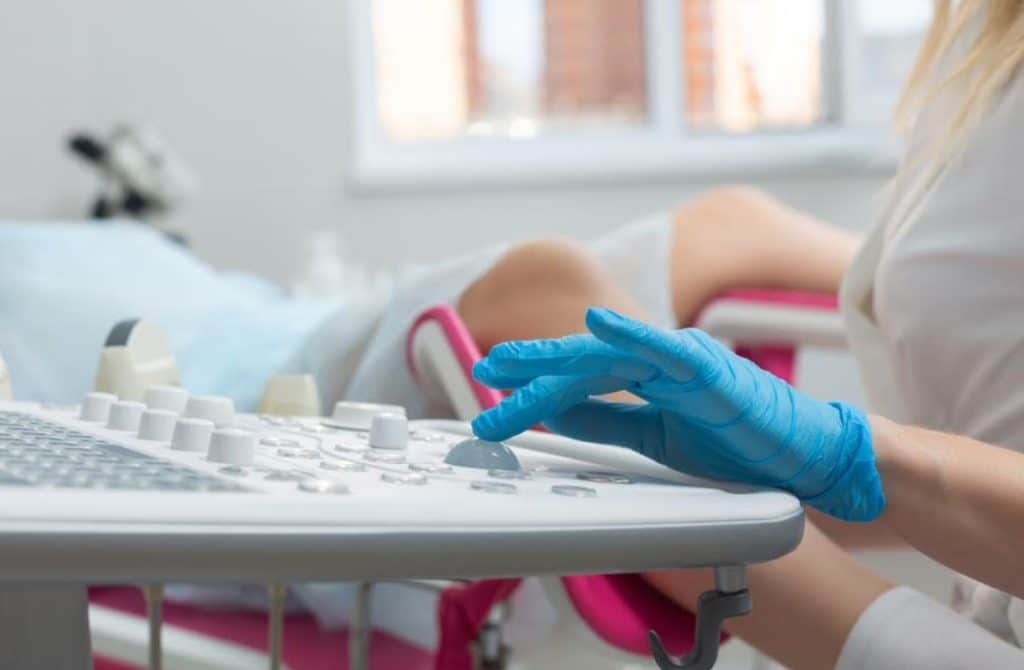
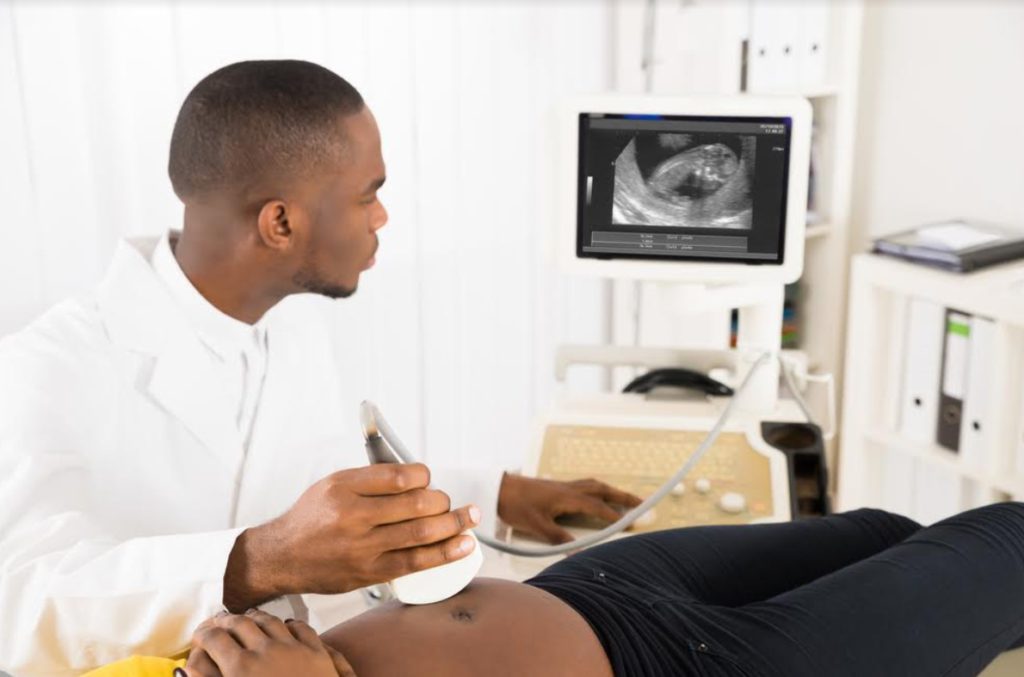
Intrauterine pregnancy is typically monitored through regular prenatal care, which includes regular check-ups with an obstetrician or midwife and various diagnostic tests to assess the health of the mother and the developing fetus. One of the most common tests used to monitor intrauterine pregnancy is an ultrasound, which uses sound waves to create images of the developing fetus and can detect any potential abnormalities.
How to confirm an Intrauterine pregnancy
Using specific tests, it is possible to confirm an intrauterine pregnancy. One of the most common and widely used tests for confirming an intrauterine pregnancy is ultrasound. The following tests can confirm an intrauterine pregnancy:
Fetal Heart Activity
Examining fetal heart activity is another way to confirm an intrauterine pregnancy. After 6 weeks of pregnancy, fetal heart activity is visible. The heart rate of a fetus increases every week, and the average heart rate ranges from 100 to 120 beats per minute.
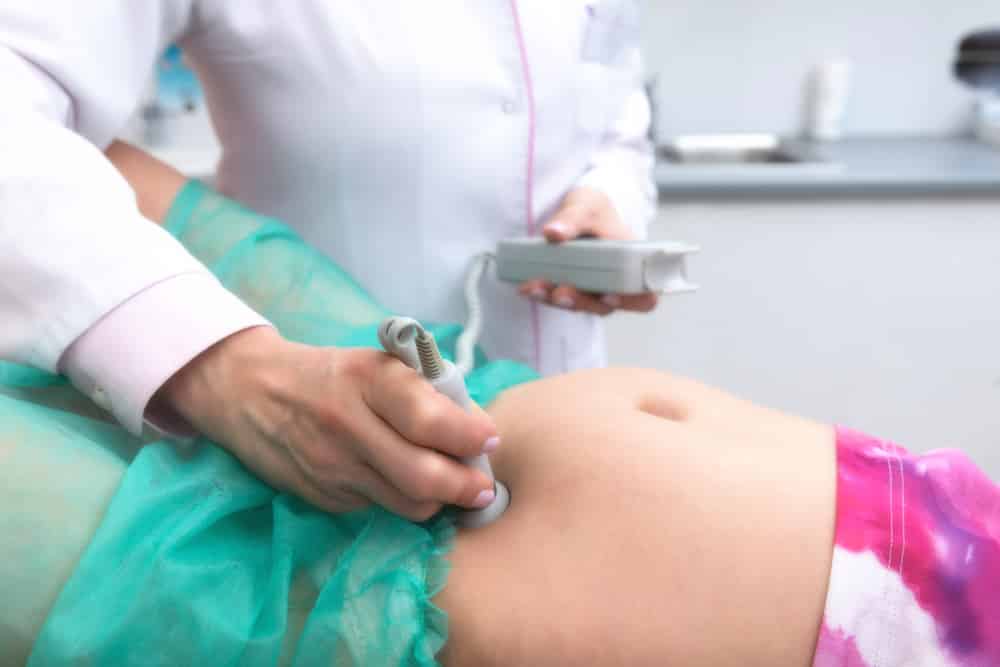
A visible Yolk Sac
With a transvaginal ultrasound, it is possible to identify a visible yolk sac at about the 5th week of gestation. This yolk sac provides nutritional support to the developing embryo until the placenta forms.
Complications that can occur in intrauterine pregnancies
While intrauterine pregnancies are generally safe and normal, specific risks and complications can arise.
Some of these complications include:
1. Miscarriage
This is one of the most common complications of intrauterine pregnancy. A miscarriage occurs when the developing fetus stops growing or dies before the 20th week of gestation.
Although miscarriages often result from chromosomal abnormalities, they may also arise due to maternal health conditions such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, or infections.
2. Preterm Labor
This is another potential complication of intrauterine pregnancy, which occurs when the mother enters labor before the 37th week of pregnancy. Preterm labor can also increase the risk of complications for the developing fetus. Some of the fetal complications of preterm labor include respiratory distress syndrome and neurological problems.
3. Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR)
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) is a condition where the developing fetus is smaller than expected for its gestational age. IUGR can occur for various reasons, including maternal health problems, placental problems, and genetic abnormalities. IUGR can increase the risk of complications for the developing fetus, including respiratory distress syndrome and neurological problems.
4. Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a potentially life-threatening complication of intrauterine pregnancy that occurs when the mother develops high blood pressure and protein in her urine after the 20th week.
Causes of complication during intrauterine pregnancy
Several factors can increase the likelihood of complications during intrauterine pregnancy. These include advanced maternal age, pre-existing health conditions such as hypertension or diabetes, and lifestyle factors such as smoking or drug use.
To minimize the risks of intrauterine pregnancy, women need to receive regular prenatal care and make lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking and avoiding alcohol and illicit drugs. Prenatal vitamins, a healthy diet, and regular exercise can also help promote a healthy pregnancy.
The Takeaway
In cases where complications do arise, there are various treatments and interventions that can be used to improve outcomes. For example, women who are at high risk of preterm labor may be prescribed medications such as progesterone to help prevent early delivery.
In cases where the developing fetus has a medical condition or abnormality, doctors may recommend additional testing or procedures such as amniocentesis or fetal surgery.
Finally, it always helps to remember that your doctors and healthcare professionals are always available to help you through every step of this journey.
You are not alone.