Birth control is very important in preventing unplanned pregnancies. There are a number of options available to consider when choosing a birth control method, and this includes an IUD or Intrauterine Device.
Although it is not advisable for every woman, IUDs are often safe and long-lasting. One other importance of IUDs is that they are not permanent. This means you can stop it or get it removed when you are ready to have children.
This article contains the necessary information you need to know about IUDs including what an IUD is, the types available, how it is inserted, risks associated with using an IUD, and lots more.
Let’s Get Started!
Table of contents:
What is an IUD?
IUD simply means intrauterine device. It is a small device shaped in form of a letter T. It is placed inside the uterus to prevent pregnancy. An IUD prevents pregnancy by preventing the sperms from reaching the eggs, thus, stopping fertilization from occurring.

An IUD can also be called an IUCD meaning intrauterine contraception device.
Are IUDs effective?
IUDs are one of the most effective methods of contraception. They have been tested to be over 99% effective in preventing pregnancy.
What are the types of IUDs?
There are five types of IUDs that are currently available. These include:
- Paragard, also known as Copper T
- Mirena
- Skyla
- Kyleena
- Liletta.
These five types can be classified into two broad categories: hormonal and non-hormonal.
The Paragard is a non-hormonal type of IUD. It is also called the Copper IUD or Copper T because it is made of copper. The copper ions contained in Paragard are released into the uterus which then creates a hostile environment for the sperm. This renders the sperm powerless and unable to fertilize the egg.
The Mirena, Skyla, Kyleena, and Liletta are examples of hormonal IUDs. They contain progestin, the synthetic form of the natural hormone, progesterone. This progestin is released into the uterus, thickens the cervical mucus, and prevents the sperm from entering the uterus, thereby inhibiting the movement of the sperm, making it difficult for it to reach and fertilize the egg. The hormone also thins the lining of the uterus, so an egg is not likely to implant on it.
What are the pros and cons of IUDs?
Pros
- IUDs are a very effective method of birth control.
- They are reversible.
- They are convenient
- They can last for a very long period of time depending on the type. The time range from 3 to 12 years.
- Ease of Access: For example, IUDs are completely free in all Government Health Centres in Nigeria.
Cons
- IUDs can be very expensive, especially if you don’t have insurance.
- They do not protect against STIs.
- The insertion process can be very uncomfortable.
Who can use an IUD?
IUDs can be used by most healthy women. They are also best for women with one partner who are at low risk of contracting an STI.
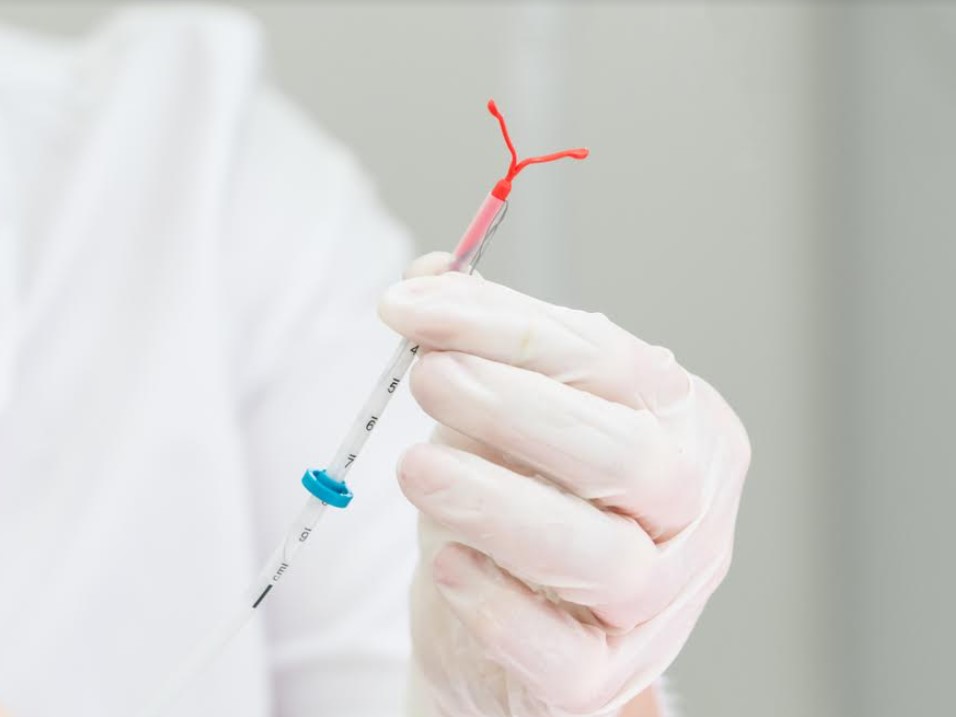
You should not use an IUD if you have any of the following:
- If you are pregnant.
- If you have an STD.
- If you have a recent pelvic inflammatory disease.
- If you are bleeding from your vagina.
- If you have cancer of the cervix or uterus.
- If you have certain blood disorders that prevent your blood from clotting.
Also,
- If you have an allergy to copper or Wilson’s disease (a disease that causes the excess accumulation of copper in the body), don’t use the Paragard IUD.
- If you have liver disease, or breast cancer (or you’re at high risk for it), don’t use any of the hormonal IUDs.
How an IUD is inserted
IUDs are usually inserted by a health care professional. These professionals are known as FP providers or Contraceptive Care providers. The whole process does not take so much time; in about 30 minutes you should be done. The insertion procedure itself takes less than 5 minutes.

The process of inserting an IUD starts with you putting your feet in stirrups. The doctor places a speculum into your vagina to keep your vagina open. The IUD is then placed into a small tube which helps in the insertion process. The tube containing the IUD is inserted into the vagina and pushed up through the cervix and then to the uterus. Once the tube is in the uterus, the IUD is pushed out of the tube and the tube is pulled out of the uterus.
How to prepare for your IUD insertion appointment
The process of inserting an IUD can be very uncomfortable, so it is necessary that you make adequate preparation for it. The following tips can help you prepare adequately for your appointment:
- Wear one of your most comfortable clothes. Think of one that is very easy to get off and back on.
- Get an over-the-counter (OTC) pain relief or one prescribed by your doctor. This will help you relieve any pain that you may feel after the procedure.
- Taking the pain relief before the procedure can also help.
- You will need a heating pad, some pads or panty liners after the procedure, so it’s best to get them ready before the procedure.
Risks associated with using an IUD
The following risks are possible with the use of an IUD, although the chance of them occurring is very low.
- Infection: There’s a small chance that you will have an infection after an IUD insertion. This risk is highest within the first 20 days after the insertion and then drops drastically.
- Perforation: The risk of the IUD getting perforated during insertion is very low. It occurs in about 1 to 2 in 1000 women.
- Expulsion: If you have never been pregnant or are under the age of 20, the chances of your IUD falling out of place is high compared to those who are not in this category.
When can the IUD be removed?
You can remove your IUD at any time you feel like doing so. Just make an appointment with your doctor to get it removed.
Your IUD can protect against pregnancy as long as you have it in. It is advisable not to keep it longer than its expiration date. The expiration date depends on the type and brand of IUD that you’re using.
When to consult a doctor
IUDs don’t pose any serious threat or complication to you but you should watch out for some signs that may indicate that something has gone wrong. Call your doctor if you notice any of the following:
- If you have severe pain in your stomach or lower abdomen.
- If the IUD feels like it has shifted or is coming out.
- If penetrative sex becomes more painful.
- If you bleed during or after sexual activity.
- If the IUD string feels longer or shorter.
- If there’s a change in the appearance of your vaginal discharge.
- If you have a fever or chills.
- If you have unprotected sex with someone who has an STI.
- If you think you are pregnant.
Conclusion
IUDs are an effective method of birth control. Consult your doctor to know if this option is good for you and when you can get it done. If you also notice any side effects after getting an IUD, see your doctor.

