Birth control is a great way for you and your family to plan and prepare for the coming of your baby. In addition to promoting maternal and child health, an effective birth control option also improves economic and social stability. For some women, the best birth control option is to tie the fallopian tubes via tubal ligation.
Nevertheless, studies show that some women still have children after a tubal ligation. Interestingly, this is not some myth or tale, it really does happen.
The article contains all you need to know about the fallopian tubes, what it does, how pregnancy occurs. Furthermore, there’s a section on the possibility of becoming pregnant without the fallopian tubes.
Table of contents
What are fallopian tubes?
The fallopian tube is the same as the uterine tube or oviduct. It is an integral part of the female reproductive system that comes in pairs, one on the right and the other on the left. The fallopian tube is a long narrow duct that transports sperm cells to the eggs during the fertilization process.

Each fallopian tube is about 4-5 inches long and about 0.2-0.6 inches wide. In addition to transporting the sperm to the eggs, it also provides the right environment for fertilization and conception,
Parts of the Fallopian Tubes
Each tube has five distinct parts; the fimbriae, the infundibulum, the ampulla, the isthmus, and the uterine part. The fimbriae are fingerlike projections close to the ovaries. They contact the ovary during ovulation to guide the released egg towards the infundibulum.
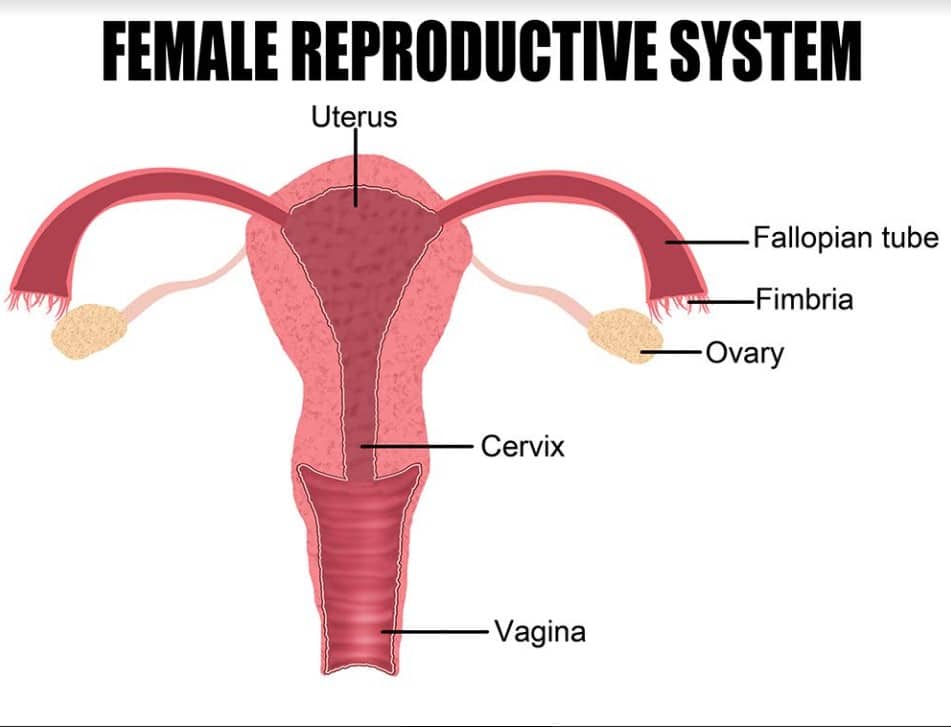
From the infundibulum, the eggs move to the ampulla. If fertilization takes place, it occurs at the ampulla. The isthmus connects the ampulla to the uterus. The uterine part of the fallopian tube lies in the upper region of the uterus. It leads to the uterine cavity where fertilized eggs attach and grow.
How Does Pregnancy Occur with Fallopian Tubes?
Women are able to get pregnant from puberty. This is when the menstrual cycle begins. For a natural pregnancy to take place there has to be sexual intercourse between a man and a woman.
When this occurs, the man ejaculates and deposits sperms into the woman and it travels through the vagina to the uterus until it gets to where the eggs are, which at this time is somewhere in the fallopian tube. Normal fertilization takes place in the ampulla of the fallopian tube.
Subsequently, the fertilized egg moves to the uterus. Eventually, this fertilized egg implants and develops in the uterus.
Is it Possible to Get Pregnant Without Fallopian Tube?
Seeing the great function that the fallopian tube performs in the process of fertilization, one can conclude that the fallopian tube is indispensable in the occurrence of a natural pregnancy. Some women are born with one or both of their fallopian tubes absent while some have had their tubes ligated to prevent further pregnancy. This raises the question of the possibility of women like this becoming pregnant in the future.
It is possible for women without fallopian tubes (either by natural occurrence or medical intervention) to become pregnant. This is possible via In-Vitro fertilization (IVF).
IVF is one of the many types of assisted reproductive technology (ART). It works by using a combination of medical and surgical procedures to help sperm fertilize an egg and also help the fertilized egg implant in the uterus. It involves collecting matured eggs from the woman and fertilizing them with sperm in the lab and then transferring the fertilized egg back to the uterus.

IVF Procedure
To undergo an IVF procedure, you have to go through the following steps:
Testing stage
In this stage, you and your partner will undergo various fertility tests and also some infectious disease screening. The fertility tests help to know the quality and quantity of your eggs that are available for fertilization. Your partner’s semen will also be tested (semen analysis).
Follicle stimulation stage
If all the tests go well and you’re fit for an IVF, certain prescribed medications stimulate the ovarian follicles to produce multiple eggs. In a normal menstrual cycle, one egg with one follicle develops, but in IVF, the higher the number of follicles stimulated with the medications, the higher the success rate of the procedure.
At this point, different medications stimulate your ovaries to develop more than one egg at a time; medications to help mature the stimulated eggs; medications to prevent premature ovulation of the eggs, and medications to prepare the lining of your uterus for implantation.
Your doctor will guide you to know which drug to use at each point in time.
Egg retrieval stage
When the eggs are ready for fertilization just before ovulation takes place, the matured eggs are retrieved through a needle that is connected to a suction device. Multiple eggs can be collected at this stage.
Sperm retrieval stage
On the morning when your eggs are being retrieved for fertilization, your partner’s semen will also be collected. The sperms are then separated from the semen in the lab.
Egg fertilization stage
After the egg and the sperm have been retrieved, the egg is then fertilized in vitro with the sperm. Two available techniques for this fertilization include:
- Conventional insemination: where the eggs and sperms are mixed and incubated over the night.
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection: This involves the direct injection of one healthy sperm into one matured egg.
Embryo transfer stage
Following a successful fertilization stage, the fertilized eggs known as embryos, are then returned to the uterus for implantation. The embryo transfer stage is the final phase of the IVF process. After this, you would wait for the result.
Conclusion
Pregnancy is possible even after you might have had your tubes tied; although this may cost you more if you have not tied your tubes.
You can speak with your doctor to know the chances of your IVF being successful and the risks associated with it.

