During pregnancy, your body has one important function; ensuring that your baby gets all the nutrients needed for proper development. To achieve this, your body grows a temporary organ called the placenta.
To perform its unique functions, the placenta needs to be positioned in the right place at the right time, and for the right period. Most times, the placenta can either be in an anterior position or a posterior position.
In this article, we’d talk about the posterior placenta; what it is, how it functions, and the possible effects on pregnancy and childbirth.
Read on to learn more!
Table of contents
What is Posterior Placenta?
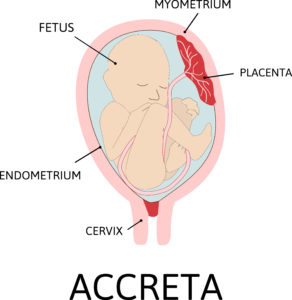
The term, posterior placenta, simply refers to a placenta that is attached to (or located at) the back of the uterus during pregnancy.
Thankfully, a posterior placenta is not a cause for concern during pregnancy. In fact, some mothers prefer this placenta position because it allows them to feel stronger fetal movements and baby kicks compared to those with anterior placentas.
What Does the Placenta Do?
The placenta is a feto-maternal organ that develops during pregnancy and is tasked with one primary function as you expect your little one. The primary function of the placenta is oxygen supply to your little one and waste removal from his/her system during pregnancy.
In addition to its transport function, the placenta also secretes various hormones like Progesterone that maintains pregnancy, and Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin (hCG) which serves as the chemical basis for positive pregnancy tests.
Does The Posterior Placenta Affect Pregnancy & Delivery?
In most cases, doctors agree that having a posterior placenta does not affect your pregnancy or delivery in any way. Except in extreme cases like placenta previa, the position of your placenta actually has no effect on pregnancy or delivery.
Other Placenta Locations
Like many other things in pregnancy, the location of the placenta is unique for every woman and in every pregnancy.
In addition to the posterior placenta, other positions/locations of the placenta include:
Anterior Placenta
In this instance, the placenta is positioned at the front of your uterus, between your stomach and your little one. With an anterior placenta, it is often more difficult to monitor fetal movements or feel your baby’s kicks. Thankfully, it is also normal and does not affect your pregnancy or delivery in any way.
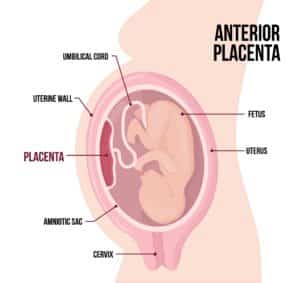
Fundal Placenta
In this position, the placenta is attached to the fundus at the top of your uterus. The fundal placenta may be further divided into:
- Fundal-anterior: when the placenta is located at the top but also extends to the front of the uterus.
- Fundal-posterior: when the placenta is located at the top but also extends to the back of the uterus.
Here’s the good news:
A fundal placenta can still perform all the required functions of oxygen delivery, waste removal, and hormone secretion throughout pregnancy.
Placenta Previa
This is an abnormal placenta position.
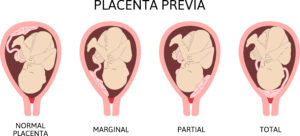
When this happens, the placenta is positioned at the cervix, thereby blocking the birth canal where your baby is supposed to pass through during delivery. Depending on how much of the cervix is blocked by the placenta, placenta previa may be subdivided into:
- Total
- Partial
- Marginal
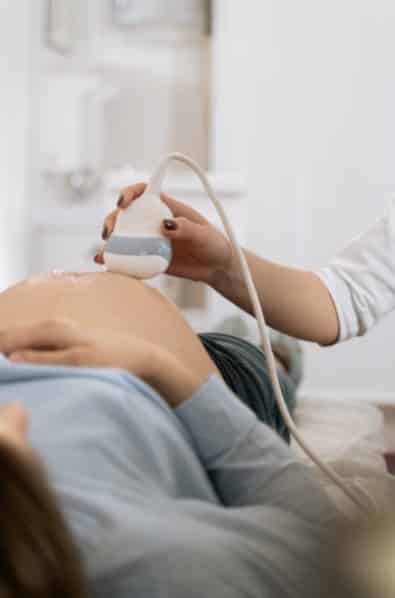
How to Determine Your Placenta Position
As we mentioned earlier, the position of the placenta is unique for every woman and in every pregnancy. Nonetheless, you can determine your placenta location at the 12th week of pregnancy through a routine ultrasound scan.
With your doctor’s assistance, you can find out the location of your placenta during an antenatal clinic.
Conclusion
Finally, it is important to remember that a posterior placenta is nothing to worry about during pregnancy. In fact, a posterior placenta performs every expected placenta function during pregnancy. As a plus, having a posterior placenta may even help you feel closer to your little one because you get to feel most fetal movements and those strong baby kicks. You can read more on Eating Placenta here
Enjoy the journey, Mama.
References
- Zia, Shumaila. “Placental Location and Pregnancy Outcome.” Journal of the Turkish German Gynecological Association, AVES, 1 Dec. 2013, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3935544/
- Cross JC: Formation of the placenta and extraembryonic membranes, Ann N Y Acad Sci 857:23, 1998.
- Kazandi M: Conservative and surgical treatment of abnormal placentation: report of five cases and review of the literature, Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 37:310, 2010.
- How your fetus grows during pregnancy. (2020).
- acog.org/patient-resources/faqs/pregnancy/how-your-fetus-grows-during-pregnancy
- Perlman N. (2019). Retained placenta after vaginal delivery: Risk factors and management. DOI:
- 10.2147/IJWH.S218933
- Benirschke K, Kaufmann P: Pathology of the Human Placenta, ed 4, New York, 2000, Springer-Verlag.